This post first appeared on Risk Management Monitor. Read the original article.
As the Trump administration wages an economic battle with China in the form of reciprocating tariffs and other economic measures, it may not be a great time to be an American company operating in China. The US-China Business Council (USCBC), an organization made up of 200 U.S. companies that do business with China, released its annual member survey, finding the trade dispute—and the ongoing political tensions underlying it—are a huge concern for these companies and may be adding to worries about doing business in China.
Since the Trump administration declared a tariff on billions of dollars of Chinese exports in June 2018, the United States and China have traded retaliatory economic measures. Negotiators from the countries are preparing to meet in October, hoping to break a deadlock, even as each side moves to put pressure on the other’s economy.
Last month, President Trump announced increased tariff rates on Chinese imports, and tweeted that American companies were “hereby ordered to immediately start looking for an alternative to China, including bringing your companies HOME and making your products in the USA.” Some U.S. business groups condemned the moves and the president’s rhetoric, including the National Retail Federation. “It’s impossible for businesses to plan for the future in this type of environment,” said David French, the federation’s senior vice president of government affairs. These moves are an outgrowth of continued tensions, both economic and political, between the two countries.
It is no wonder then, that between 2018 and 2019, the percentage of USCBC members who said that their company’s business had been affected by US-China “trade tensions” increased from 73% to 81%. Of the reasons companies reduced or stopped planning investment in China in the past year, 60% of respondents cited “increased costs of uncertainties from US-China tensions.”
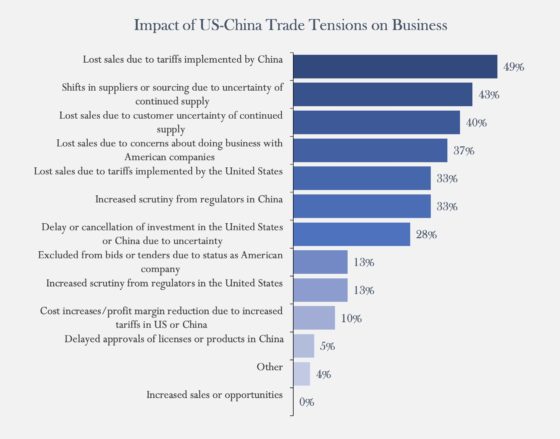
Among the real-world results of the trade dispute, USCBC members reported that the biggest impact was “lost sales due to tariffs implemented by China” (49%) and “shifts in suppliers or sourcing due to uncertainty of continued supply” (43%). The majority of the other concerns have to do with uncertainty or stigma attached to U.S. companies in China. Additionally, 26% of respondents projected that their current year revenue from China would decrease, compared to 9% in 2018.
The USCBC reported that “respondent optimism about China market prospects five years from now is at a historic low,” with the country’s stringent regulatory environment posing the largest driver of long-term doubt for U.S. companies. Indeed, the survey showed that, for 2019, 14% had a pessimistic or somewhat pessimistic five-year outlook, while 21% were neutral, an increase of 5% for both since 2018. However, the trade disputes are a major driver of short-term pessimism.
Also, when asked about cyber-related issues with doing business in China, 64% of respondents reported that “U.S.-China political tensions” were their biggest worry. And with good cause: According to cybersecurity firm Crowdstrike’s 2019 Global Threat Report, in the past year, the firm “observed an increasing operational tempo from China-based adversaries, which is only likely to accelerate as Sino-U.S. relations continue to worsen.”
And the impact reaches far broader than just companies that do business in China, like the members of the USCBC. As reported in the Risk Management article “The Business Impact of Trump Tariffs,” because many companies have complex, interconnected international supply chains, the trade dispute has a much broader effect on a wider array of businesses and industries. For example, a tariff on Chinese solar panels does not just hurt Chinese solar panel companies, it hurts U.S. manufacturers that supply parts for those panels, and U.S. companies that rely on components from Chinese manufacturers are affected as well.

